See below
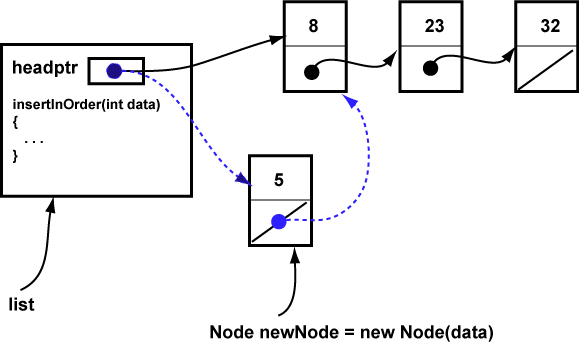
The second case is when the new value is less than the one presently in the first node. The diagram shows an existing list with its pointers in black and a new node that needs to be first. The blue pointers show the desired result.
public class OrderedLinkedList
{
private Node headPtr = null;
// The constructor creates an empty list
public OrderedLinkedList()
{
headPtr = null;
}
// various methods left out
// Insert one Node containing data
// into the list in ascending order.
// Duplicates are allowed.
public void insertInOrder( int data )
{
// Create the node to be inserted
Node newNode = new Node( data );
newNode.setNext( null );
// CASE 1: insert into an empty list
if ( headPtr==null )
{
headPtr = newNode;
return;
}
// CASE 2: data is less than current first
else if ( )
{
return;
}
// CASE 3:
// CASE 4:
}
}
Fill in the blanks to detect case 2 and then to link the new node at the head of the list.
Use the getValue() and setNext() methods of Node.