It does not point to another Node.
For it, next is null.
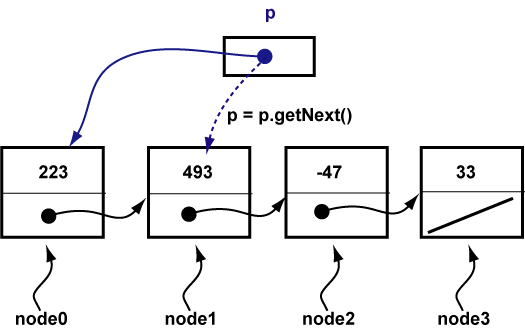
Linked lists can get very long. This calls for a loop.
Here is our program (again) that now uses a loop to visit each Node.
public class ChainMaker
{
public static void main ( String[] args )
{
Node node0 = new Node( 223 );
Node node1 = new Node( 493 );
Node node2 = new Node( -47 );
Node node3 = new Node( 33 );
node0.setNext( node1 );
node1.setNext( node2 );
node2.setNext( node3 );
node3.setNext( null ); // not needed. Here as a reminder.
// Traverse the Linked List in a loop
Node p = node0;
while ( _________________ )
{
System.out.print( p + ", " );
p = p.getNext();
}
System.out.println( "\nEnd of List");
}
}
As with many loops, there are three aspects that work together:
p must be set up correctly.while must detect the ending condition.p must be done correctly.The program is not quite complete. Loop aspect 2 is missing. What statement should go in the blank?
p = p.getNext(); p = node1; p.getNext != null p != null