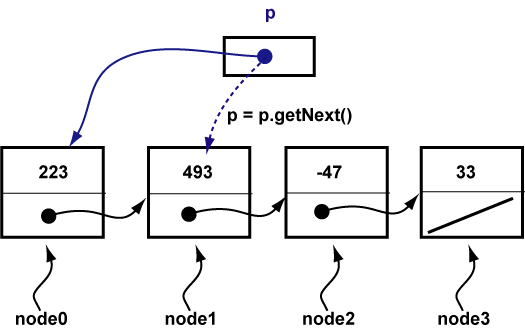
p = p.getNext();
This advances p so that it points to the Node containing -47.
// Point to the first node
Node p = node0;
System.out.print("Node 0: " + p );
// Point to the second node
p = p.getNext();
System.out.println("Node 1: " + p );
// Point to the third node
p = p.getNext();
System.out.println("Node 2: " + p );
Here is a program that advances p through the Nodes from first to last:
public class ChainMaker
{
public static void main ( String[] args )
{
// Construct four nodes
Node node0 = new Node( 223 );
Node node1 = new Node( 493 );
Node node2 = new Node( -47 );
Node node3 = new Node( 33 );
// Link the nodes into a chain
node0.setNext( node1 );
node1.setNext( node2 );
node2.setNext( node3 );
node3.setNext( null );
// Traverse the Linked List
Node p = node0;
System.out.print("Node 0: " + p );
p = p.getNext();
System.out.print(", Node 1: " + p );
p = p.getNext();
System.out.print(", Node 2: " + p );
p = p.getNext();
System.out.println(", Node 3: " + p );
}
}
This program prints out:
Node 0: 223, Node 1: 493, Node 2: -47, Node 3: 33
A systematic visit to each node of a data structure is called a traversal of the data structure. The data structure can be any of many types of data structures and there are many things a traversal can do with each node, (not just print).
What is unique about the last Node on the list?