Oh... about four.
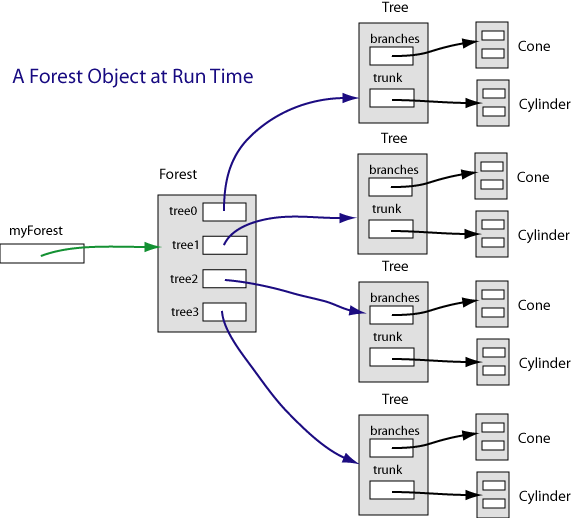
Some forests have more than four trees. But for us, let's stick to four.
A more realistic Forest object would have many trees, and this would call for
an array or other data structure.
Those are topics of future chapters.
// Forest.java
//
public class Forest
{
// instance variables
private Tree tree0=null, tree1=null, tree2=null, tree3=null;
...
}
Our Forest object is composed of four reference variables
that each point to a Tree.
Although you think of a Forest as being composed of four objects,
what it really has is references to those objects
(which in turn reference yet other objects.)
When a Forest is complete there will be 13 objects:
a Forest object,
composed of four Tree objects,
each composed of a Cone object and a Cylinder object.
(Review: ) The reference variables of Forest are initialized to null.
What does null mean?