A regular polygon is one where all angles are equal and all sides are equal.
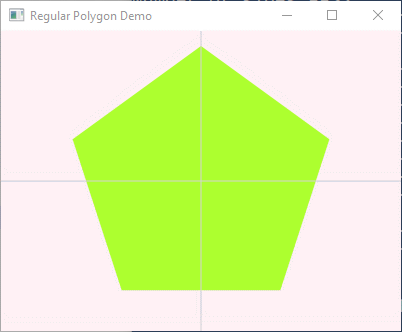
Here is a program that draws a regular polygon.
The vertices are equally spaced along an imaginary circle
with a radius held in the variable radius.
The X value of a vertex is calculated using the sine of the current angle,
and the Y values is calculated using the cosine.
The angle starts out at 90° so that the peak of the polygon is drawn at the top
and so that the polygon is symmetrical about its vertical axis.
The calculation for Y looks a bit odd:
double y = -radius*Math.sin( theta ) + sceneCenterY;
but this is because y increases going downward.
import javafx.application.*; import javafx.stage.*; import javafx.scene.Scene; import javafx.scene.shape.*; import javafx.scene.paint.*; import javafx.scene.layout.*; import java.util.Scanner; public class RegularPolygon extends Application { int N = 0; // number of sides public void init() { Scanner scan = new Scanner( System.in ); System.out.print("Number of sides ->"); N = scan.nextInt(); } public void start( Stage primaryStage ) { double sceneWidth = 400.0, sceneHeight = 300.0; double sceneCenterX = sceneWidth/2; double sceneCenterY = sceneHeight/2; // size of the polygon double radius = Math.min( sceneWidth, sceneHeight)*0.45; // array of vertices x,y, x,y, x,y // in counter-clockwise order double[] vertices = new double[ 2*N ]; for ( int j=0; j<N; j++ ) { double theta = j*2*Math.PI/N + Math.PI/2; double x = radius*Math.cos( theta ) + sceneCenterX; double y = -radius*Math.sin( theta ) + sceneCenterY; vertices[ 2*j ] = x; vertices[ 2*j+1 ] = y; } Polygon polygon = new Polygon( vertices ); polygon.setFill( Color.GREENYELLOW ); // Lines through center of scene Line xAxis = new Line( 0, sceneCenterY, sceneWidth, sceneCenterY ); xAxis.setStroke( Color.LIGHTGRAY ); Line yAxis = new Line( sceneCenterX, 0, sceneCenterX, sceneHeight ); yAxis.setStroke( Color.LIGHTGRAY ); Pane pane = new Pane( polygon, xAxis, yAxis ); Scene scene = new Scene( pane, sceneWidth, sceneHeight, Color.LAVENDERBLUSH); primaryStage.setTitle("Regular Polygon Demo"); primaryStage.setScene( scene ); primaryStage.show(); } }
Other things to note:
The init() function is defined in class Application
but does nothing, as defined there.
Override it to initialize things before start() is called.
To run this program from the command line:
% javac RegularPolygon.java % java RegularPolygon Number of sides --> 5 %
The array needs to have twice as many cells as vertices of the polygon,
so it has 2*N cells.
For vertex number j, two values need to be put into the array:
vertices[ 2*j ] = x; vertices[ 2*j+1 ] = y;
(Thought Question: ) Can Polygon be used for an irregular polygon?