Yes. One of the advantages of portability is that Java bytcodes can be copied unaltered to many types of computers and those computers can run the program.
public class Hello
{
public static void main ( String[] args )
{
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
If you have already figured out how to create, compile and run Java programs on your computer, you can skip the rest of this chapter. The screen-shots in this chapter are from Windows 10. Other Windows systems are similar.
It is useful to create a directory for Java programs directly under C: using File Explorer. A useful name for the directory might be JavaSource.
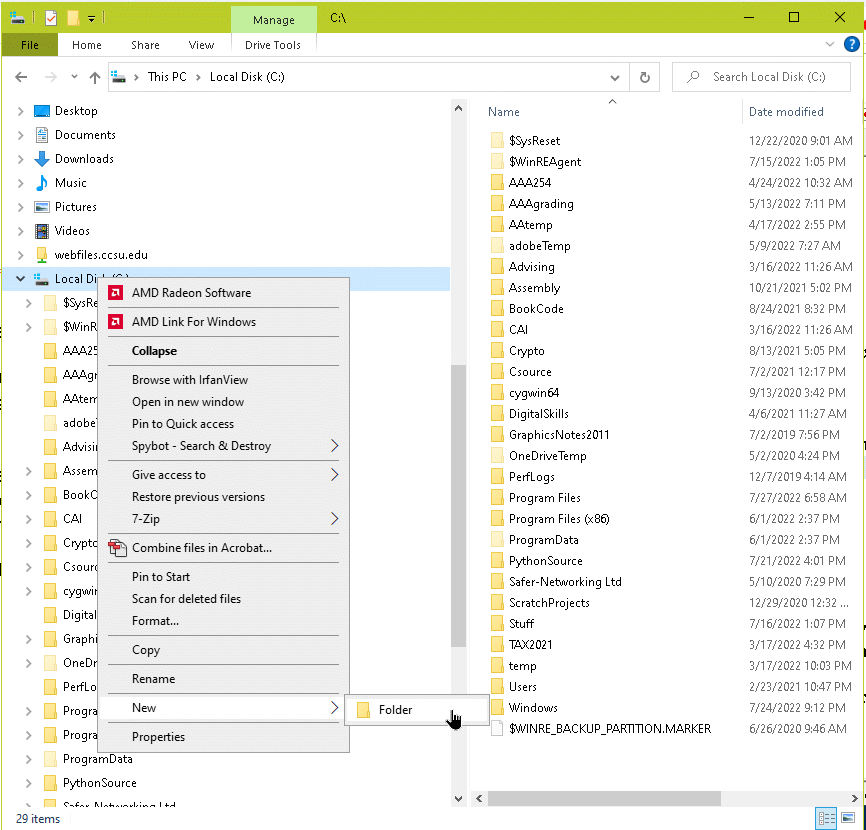
Say that you have created the program using a text editor and saved it in a file Hello.java and that the file is located in the disk directory C:\JavaSource. You can use any directory you can access. The directory can have any name.
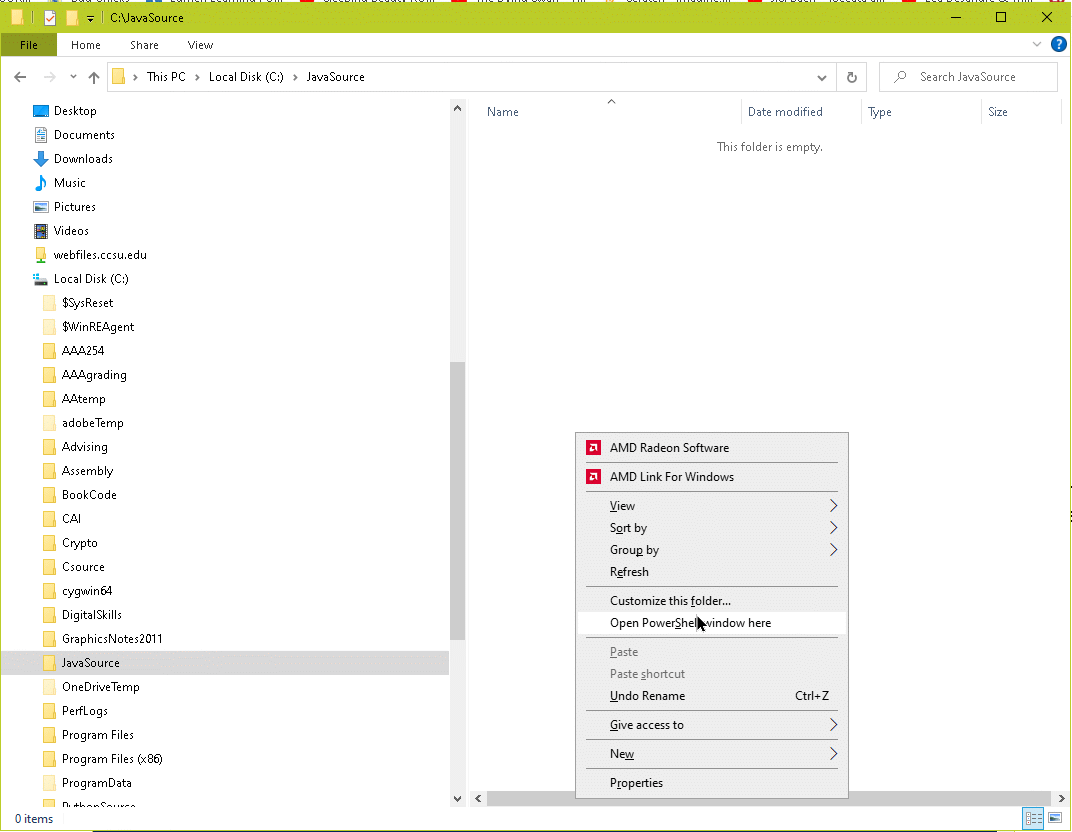
Start a command prompt window in that directory. On a Windows computer this can be done by navigating to the directory using File Explorer, putting the mouse pointer in the display of the directory, and doing shift-right-click. Select "Open Power Shell" (or similar).
Enter the DIR command at the command prompt. You should see something like this:
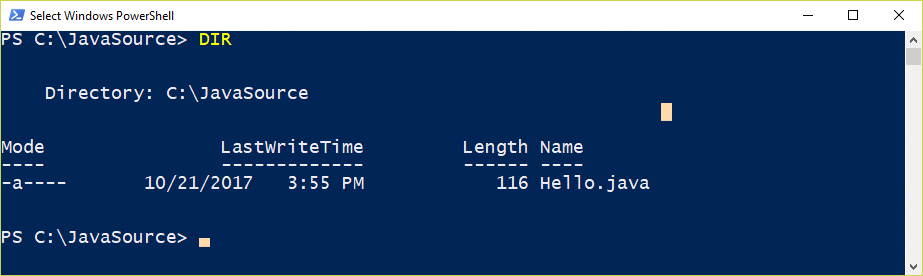
The DIR command lists the files in the DIRectory. The above shows that Hello.java is 116 bytes long. Since this is a text file, each of those bytes encodes a character or end-of-line characters.
Of course, if you have more files in the directory, DIR will show them all.
Chapter 7 shows this process in greater detail, if you need it. Better yet, find a friend or instructor than knows their way around Windows and the command prompt.
Will you see exactly the same things as above on your computer system?