Answer:
Yes.
Yes.
Now there is a one-node linked list.
Say that main() calls insertFirst() again:
// create an empty linked list
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
// insert first node
list.insertFirst( 5 );
// insert another node
list.insertFirst( 14 );
public class LinkedList
{
private Node headPtr = null;
. . .
public void insertFirst( int data )
{
Node newFirst = new Node( data ); // 1
newFirst.setNext( headPtr ); // 2
headPtr = newFirst; // 3
}
}
The statement at ( // 1 ) creates a new Node:
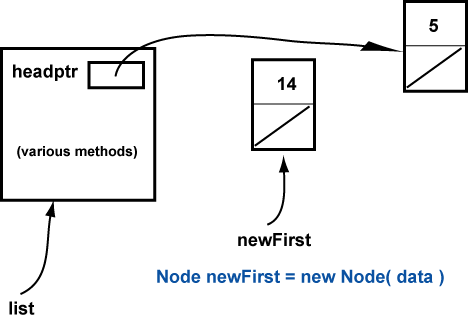
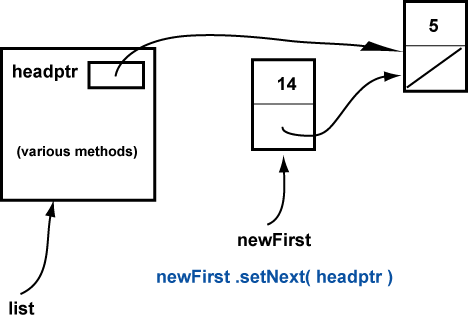
At ( // 2 ) the value in headPtr is copied into the new Node.
This copies a pointer to the current first node from headPtr into the next member of the new Node.
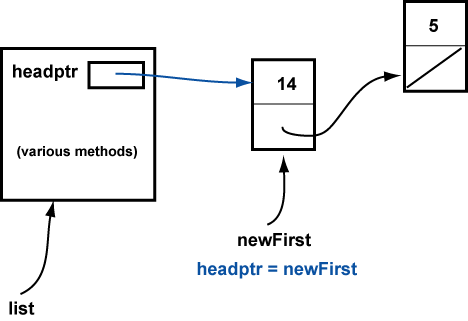
Finally ( // 3 ) a reference to the new node is copied into headPtr, and the two-node list is complete:
Could this process continued with a third node?