Answer:
Yes.
Yes.
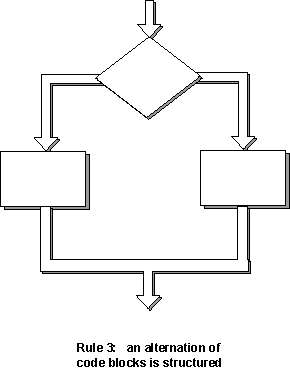
If-then-else is sometimes called alternation (because there are alternative choices). In structured programming, each choice is a code block. If alternation is arranged as in the flowchart at right, then there is one entry point (at the top) and one exit point (at the bottom). The structure should be coded so that if the entry conditions are satisfied, then the exit conditions are fulfilled (just like a code block).
Rule 3 of Structured Programming: The alternation of two code blocks is structured.
An example of an entry condition for an alternation structure is: the discriminant contains a value that is zero or positive. The exit condition might be: the correct number of roots have been computed.. The branching structure is used to fulfil the exit condition.
Can the condition which is tested (in the diamond-shaped box) be complicated?