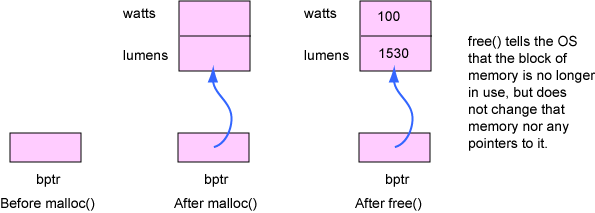
Write a main() that has a variable that
can point to struct Bulb.
Allocate memory for a struct, assign the address to the
variable, initialize and print the struct.
Use void *malloc(size_t size)
for allocating memory.
Use void free(void *address)
for deallocating memory.
You may need to include <stdlib.h> for these functions.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Bulb
{
int watts;
int lumens;
};
/* function to print a Bulb */
void printBulb( struct Bulb *b )
{
printf("watts = %d\tlumens = %d\n", b->watts, b->lumens );
}
int main()
{
/* declare and initialize a Bulb pointer */
struct Bulb *bptr;
/* allocate memory for the Bulb */
/* initialize the Bulb */
/* print the Bulb */
/* deallocate memory for the Bulb */
return 0;
}