Answer T10
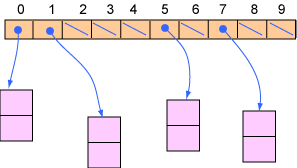
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Bulb
{
int watts;
int lumens;
};
/* function to print a Bulb */
void printBulb( struct Bulb *b )
{
printf("watts = %d\tlumens = %d\n", b->watts, b->lumens );
}
#define length 10
int main()
{
int j;
/* declare and initialize an array of Bulb pointers */
struct Bulb *bptr[length];
for ( j=0; j<length; j++ ) bptr[j] = NULL;
/* allocate memory for selected elements of the array */
/* assign values to them */
bptr[0] = (struct Bulb*)malloc( sizeof(struct Bulb) );
bptr[0]->watts = 100; bptr[0]->lumens = 1710;
bptr[1] = (struct Bulb*)malloc( sizeof(struct Bulb) );
bptr[1]->watts = 100; bptr[1]->lumens = 1530;
bptr[2] = (struct Bulb*)malloc( sizeof(struct Bulb) );
bptr[2]->watts = 175; bptr[2]->lumens = 830;
bptr[5] = (struct Bulb*)malloc( sizeof(struct Bulb) );
bptr[5]->watts = 40; bptr[5]->lumens = 505;
bptr[7] = (struct Bulb*)malloc( sizeof(struct Bulb) );
bptr[7]->watts = 50; bptr[7]->lumens = 648;
/* print the array */
for ( j=0; j<length; j++ )
if ( bptr[j] != NULL )
{
printf("Bulb %2d: ", j); printBulb( bptr[j] );
}
/* deallocate memory for the Bulb */
for ( j=0; j<length; j++ )
if ( bptr[j] != NULL )
{
free( bptr[j] );
}
return 0;
}


