Examine the following:
#include <stdio.h>
int main( void )
{
int a = 99;
int *pa ;
int *qa ;
pa = &a ;
qa = pa ;
printf("a=%d *pa=%d *qa=%d\n", a, *pa, *qa );
return 0;
}
In this example, the variable a
is an int, as previously.
But now there are two variables,
pa and qa that can
point to an int.
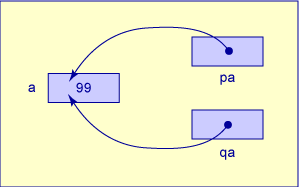
The fourth statement pa = &a
points pa to a.
The fifth statement qa = pa
copies whatever value is in pa
to qa.
This is just like any assignment statement: value on the right
of the = is copied into the variable
on the left.
Here is where you need to keep in mind pointer variable vs. pointer value.
There is a value in the variable pa .
That value (which happens to be a pointer value) is copied into another variable qa (
which happens to be a pointer variable.)
What does the program write to the monitor?