**ppv = 99
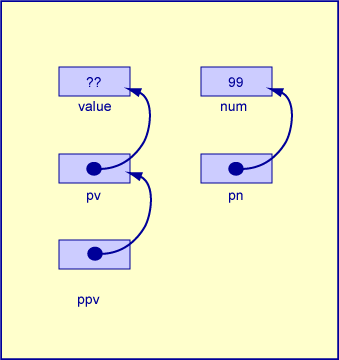
#include <stdio.h>
void main ( void )
{
int value, num = 99 ;
int *pv= &value, *pn = &num ;
int **ppv= &pv ;
**ppv = *pn; /* ugly statement */
printf("**ppv = %d\n", **ppv );
}
The statement
**ppv = *pn;
calls for an L-value (a location) on the left of the assignment operator and calls for an R-value (an integer in this case) on the right of the assignment operator.
It helps to remember that assignment statements happen in two big steps:
pn to the location that holds 99**ppv
to the variable value